Subjective Indicator Of Disease
Subjective indicator of disease. Subjective symptom one perceptible only to the patient such as pain pruritus or vertigo. Disease whose cause is unknown. There are several kinds of instruments for clinical use to assess physical status which were extensively used in dialysis studies.
The practical development of a subjective health indicator is des-cribed. Thanks for visiting The Crossword Solver. I quality of life measurements.
Number of teeth and DFT covaried with clinical indicators. They are contrasted with objective social indicators that are statistics that have some significance for measuring the quality of life from the point of view of any independent observer. Life expectancy infant mortality and subjective well-being.
Three indicators of health. A subjective indication of disease that is not obvious to an observer is referred to as a. Recent observations suggest that subjective measures of disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease IBD are often misleading.
Withdrawal ss withdrawal def. The 2 subjective indicators changed front position and gingival bleeding associated with attitudes behaviors and subjective health. 1 community periodontal index of treatment needs CPITN 2 subjectively reported change of front teeth position and 3 subjectively reported gingival bleeding.
The addition of subjective data collected in a standardized way could enable those concerned to delineate more closely the needs and problems of the community. The 2 subjective indicators changed front position and gingival bleeding associated with attitudes behaviors and subjective health. Subjective data is gathered from the patient telling you something that you cannot use your five senses to measure.
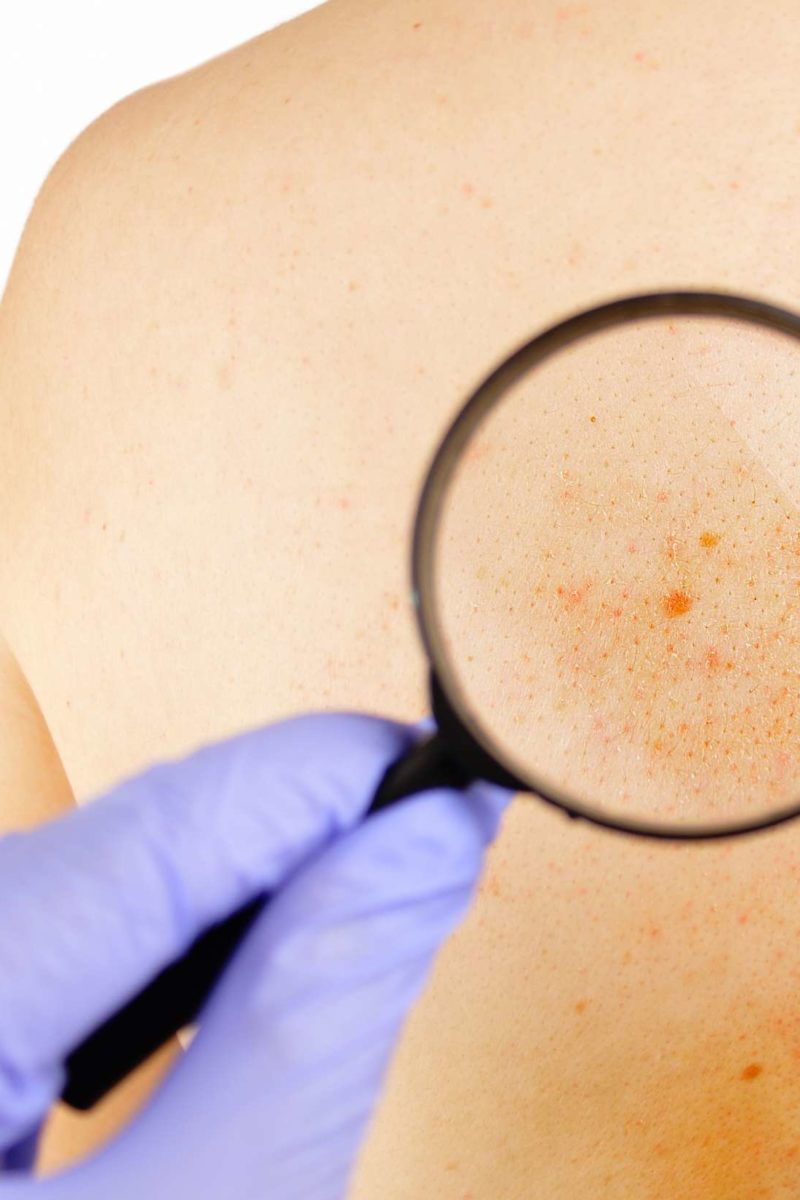
Socialization and stigmatization disease-related constraints and uncertainty symptoms and their impact on body and mind loss of body control including sexuality disease transmission and long-term impact of the disease. Body defence against injury infection or allergy marked by redness heat pain.
Cancer concerns were among the highest scored by all patients median 618.
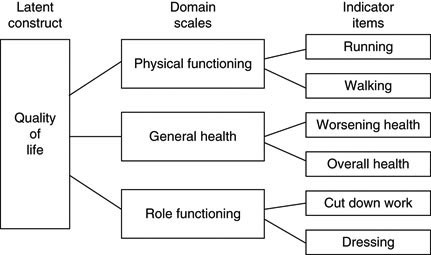
METHOD These 3 indicators were used in models with explanatory variables from 4 domains. Subjective indicator of a. Anything that accompanies X and is regarded as an indication of Xs existence. Subjective data is gathered from the patient telling you something that you cannot use your five senses to measure. 1 community periodontal index of treatment needs CPITN 2 subjectively reported change of front teeth position and 3 subjectively reported gingival bleeding. But none of the subjective measures obtained from the sample correlated with risk of death except one dimension of quality of life. Socialization and stigmatization disease-related constraints and uncertainty symptoms and their impact on body and mind loss of body control including sexuality disease transmission and long-term impact of the disease. All generic instruments to measure quality of life cover physical status through questions about ability to perform daily living activities. Use of tobacco had strong effects in all models as did high care utilization.
Body defence against injury infection or allergy marked by redness heat pain. Indicators such as morbidity and mortality are seen to require supple-mentation by more subjective assessments of need. Subjective symptom one perceptible only to the patient such as pain pruritus or vertigo. Subjective evaluation or satisfaction with a number of domains despite the fact that there were large differences between the cities in terms of objective indicators. Anything that accompanies X and is regarded as an indication of Xs existence. Use of tobacco had strong effects in all models as did high care utilization. Subjective cognitive decline SCD characterized by a very early and subtle cognitive decline prior to the appearance of objective cognitive impairment is considered to be the preclinical manifestation of Alzheimers disease AD.



























Post a Comment for "Subjective Indicator Of Disease"