In What Type Of Disease Is Specificity Of Exposure Most Likely To Be True?
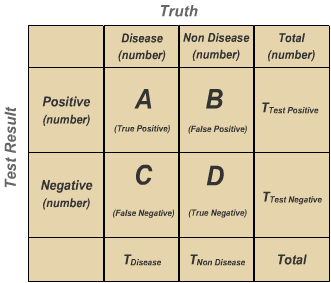
In what type of disease is specificity of exposure most likely to be true?. The person has the disease and the test is positive. The ability of a test to correctly identify people without the disease. Table 2 Specificity d bd d true negative bd true negative false positive Probability of being test negative when disease absent.
Biological plausibility There is a potential biological mechanism which explains the association. The ability of a test to correctly identify patients with a disease. Biological gradient Changes in the intensity of the exposure results in a change in the severity or risk of the outcome ie.
Specificity measures the proportion of negatives that are correctly identified. 2 cytogenetic studies that may guide molecular studies by pointing to relevant inherited or de novo chromosomal abnormalities in. A person who has been exposed.
The person does not have the disease and the test is negative. 1 whole genome screens searching for linkage of autism to shared genetic markers in populations of multiplex families families with 1 affected family member. Contact exposure to a source of an infection.
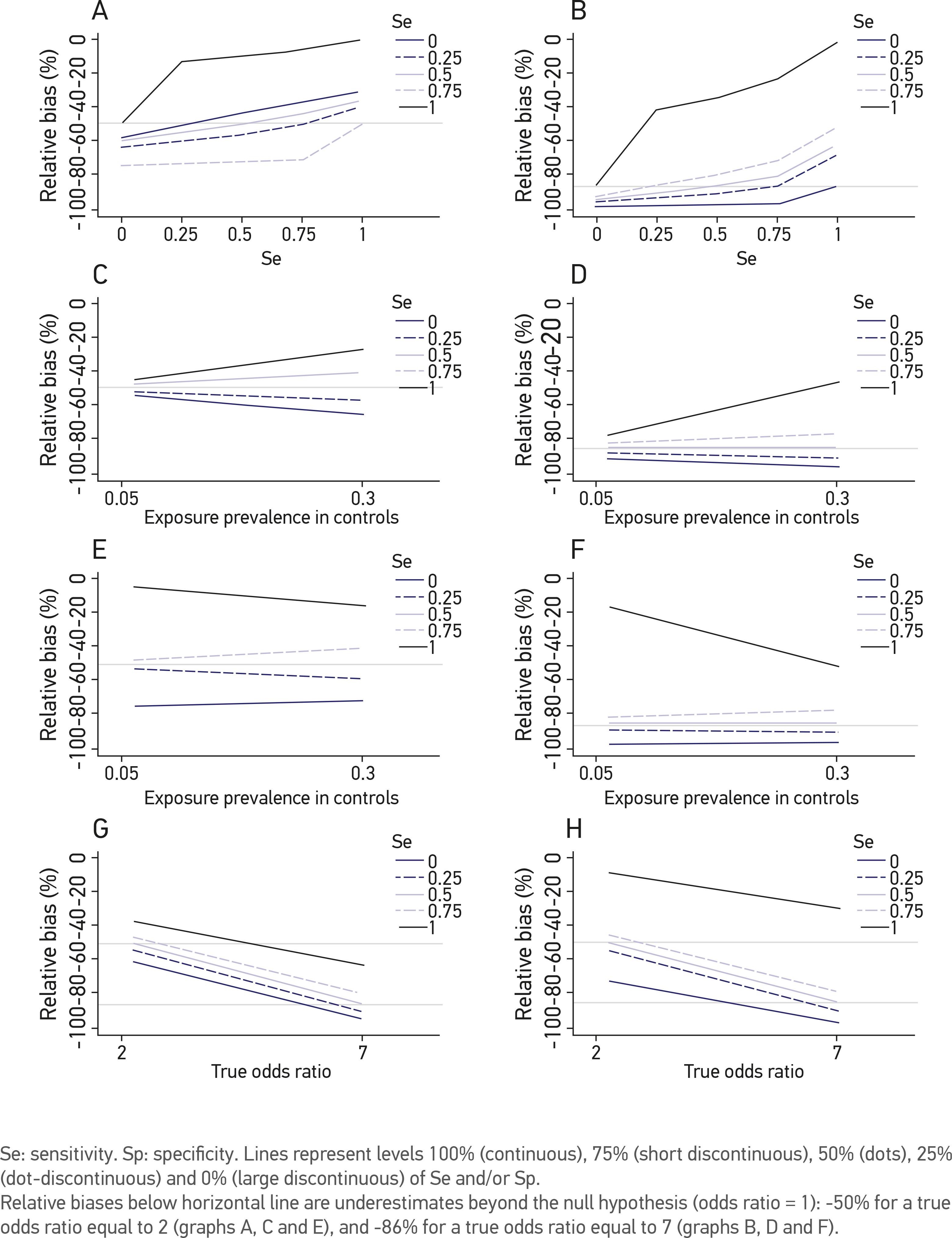
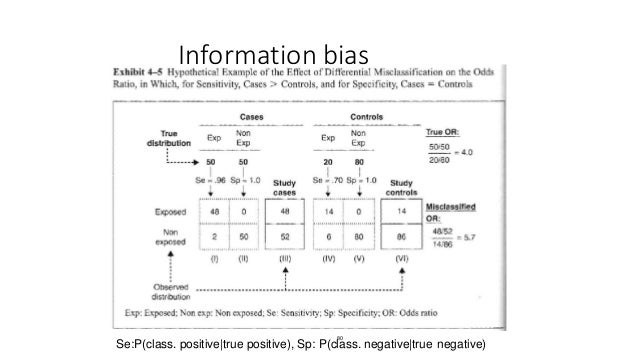
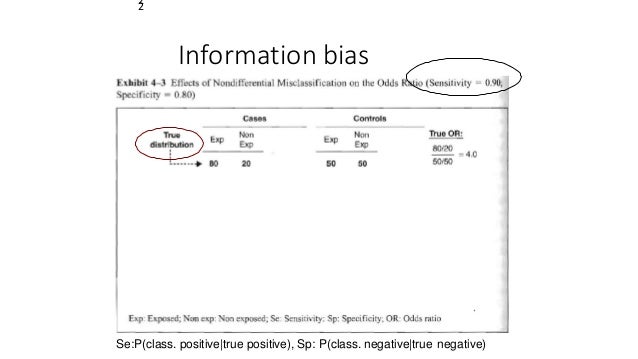
Another possible bias is information bias which arises because of misclassification of the level of exposure or misclassification of disease. The test incorrectly indicates that HIV is present in a non-infected person. Most adult-onset degenerative diseases of the nervous system are likely to be a composite of related characteristics heritable and environmental.
When an exposure has occurred the likelihood of rabies infection varies with the nature and extent of that exposure. The association of mutations in genes encoding the contractile apparatus of vascular SMCs with TAAs and dissections indicates that SMC tonus and function may be an important phenotype that influences site specificity. The ability of a test to correctly classify an individual as disease- free is called the tests specificity.
In the context of communicable disease the host-parasite relationship must be considered not only with respect to the individual host-parasite interaction but also in terms of the interrelationship between the host and parasite populations as well as those of any other host species involved. The percentage of the results that will be negative when HIV is not present.
The correlated combinations of these features constitute the trait or disease.
The ability of a test to correctly identify patients with a disease. 2 cytogenetic studies that may guide molecular studies by pointing to relevant inherited or de novo chromosomal abnormalities in. Other factors are comfortable temperature- humidity regime the hypobacterial and allergen-free air environment saturated with aeroions. The terms true positive false positive true negative and false negative refer to the result of a test and the correctness of the. The percentage of the results that will be negative when HIV is not present. Sensitivity measures the proportion of positives that are correctly identified. Any penetration of the skin by teeth constitutes a bite exposure. There are 3 main approaches to identifying genetic loci chromosomal regions likely to contain relevant genes. The null making it more difficult to detect true associations between exposure and disease.
The percentage of the results that will be negative when HIV is not present. All diagnostic tests have limitations and sometimes their use may produce erroneous or questionable results. Table 2 Specificity d bd d true negative bd true negative false positive Probability of being test negative when disease absent. The test incorrectly indicates that HIV is present in a non-infected person. The ability of a test to correctly identify patients with a disease. Contact direct exposure or transmission of an agent from a source to a susceptible host through touching eg from a human host by kissing sexual intercourse or skin-to-skin contact or from touching an infected animal or contaminated soil or vegetation. Biological gradient Changes in the intensity of the exposure results in a change in the severity or risk of the outcome ie.

























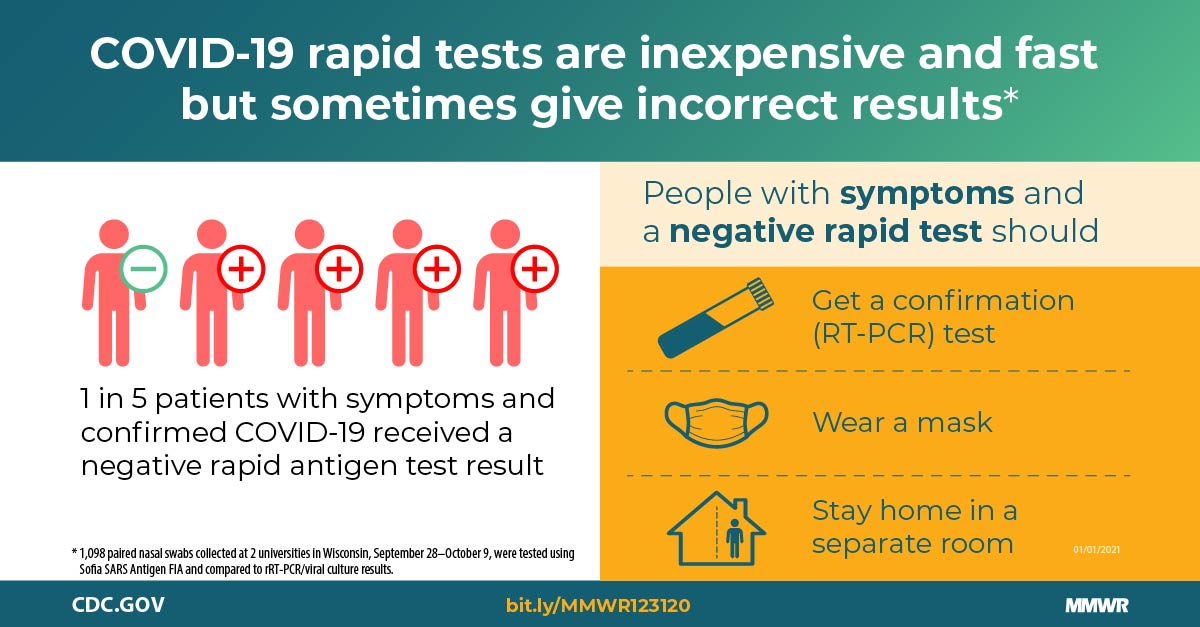
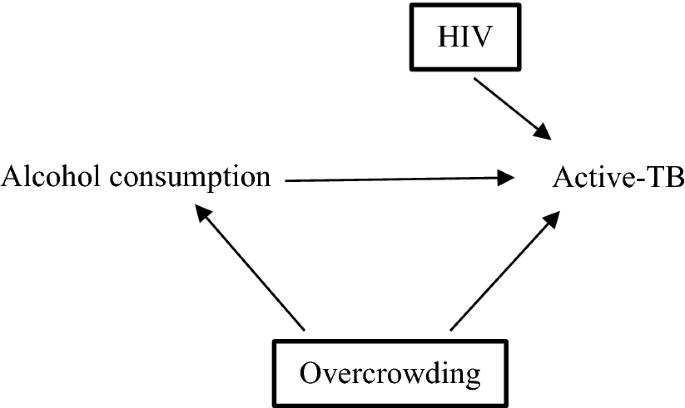
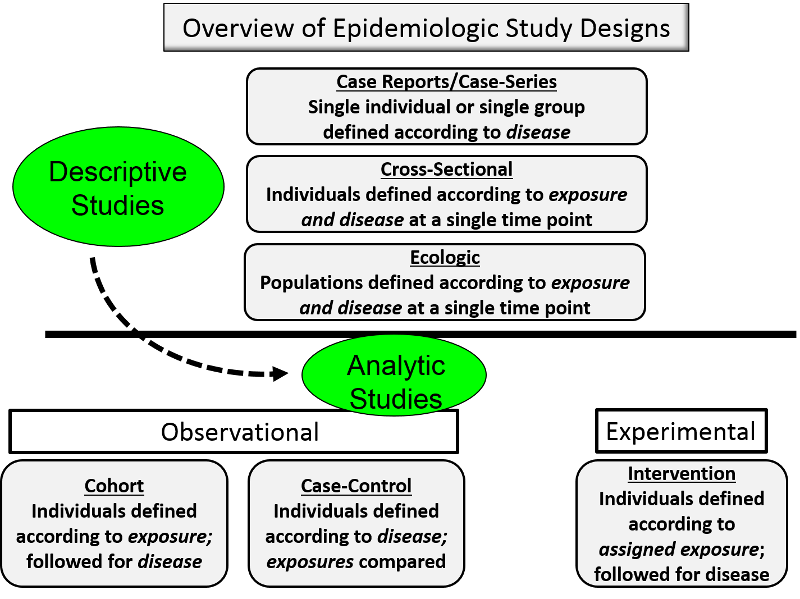
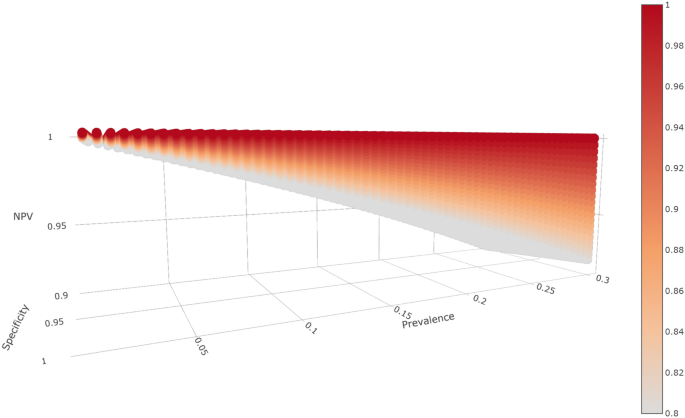
Post a Comment for "In What Type Of Disease Is Specificity Of Exposure Most Likely To Be True?"