Glanders Disease In Humans
Glanders disease in humans. Description of human glanders Clinical epidemiology and risk factors. Glanders may manifest in humans as localized pulmonary bloodstream or chronic infections CDC. Glanders is transmitted by direct invasion of abraded or lacerated skin.
Glanders is a disease caused by the bacterium Burkholderia mallei. Rarely the bacteria spread from infected animals to humans. While people can get the disease glanders is primarily a disease affecting horses.
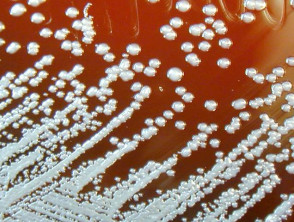
Glanders specific infectious and contagious disease of solipeds the horse ass and mule. Zoonotic transmission of B. Glanders is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Burkholderia mallei.
Glanders is an infectious disease of horses and donkeys caused by the gram-negative bacterium Pseudomonas mallei. The bacteria that cause glanders are transmitted to humans through contact with tissues or body fluids of infected animals. Common symptoms of glanders include fever with chills and sweating muscle aches chest pain muscle tightness and headache.
Glanders is primarily a disease affecting horses but it also affects donkeys mules and can be contracted by goats dogs and cats. The bacteria enter the body through the skin eyes and nose. It has been eradicated in many parts of the world.
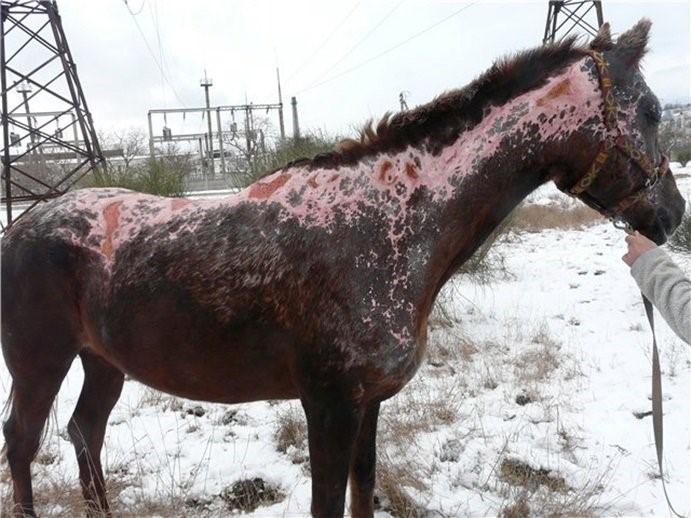
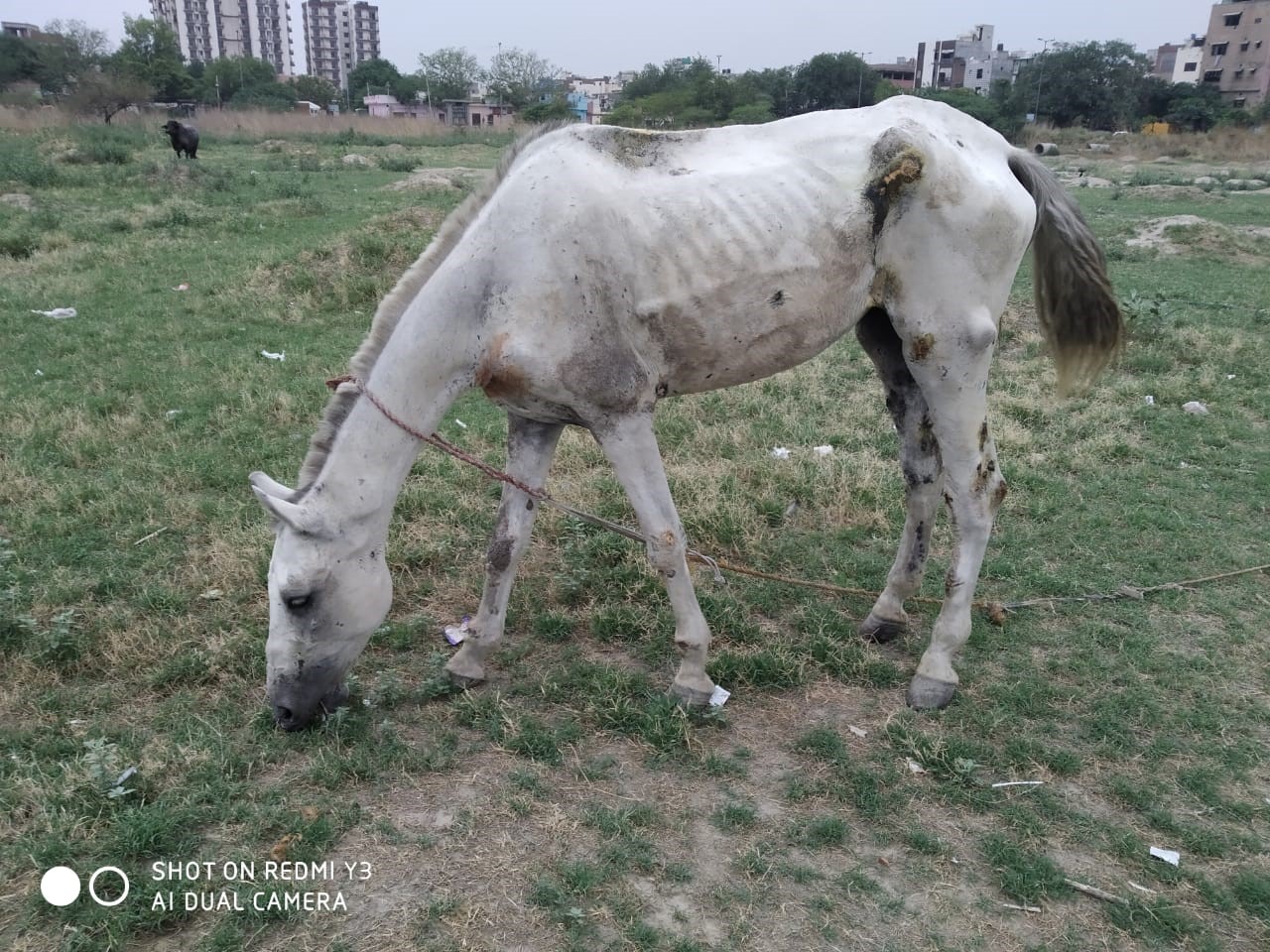
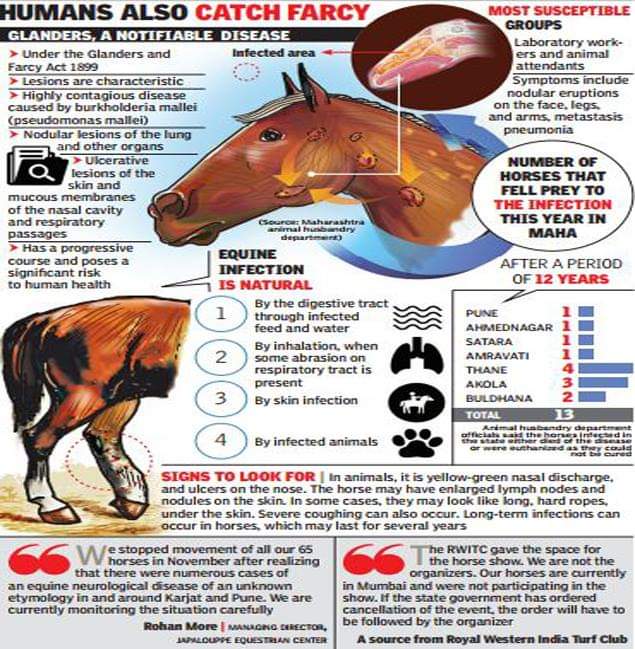
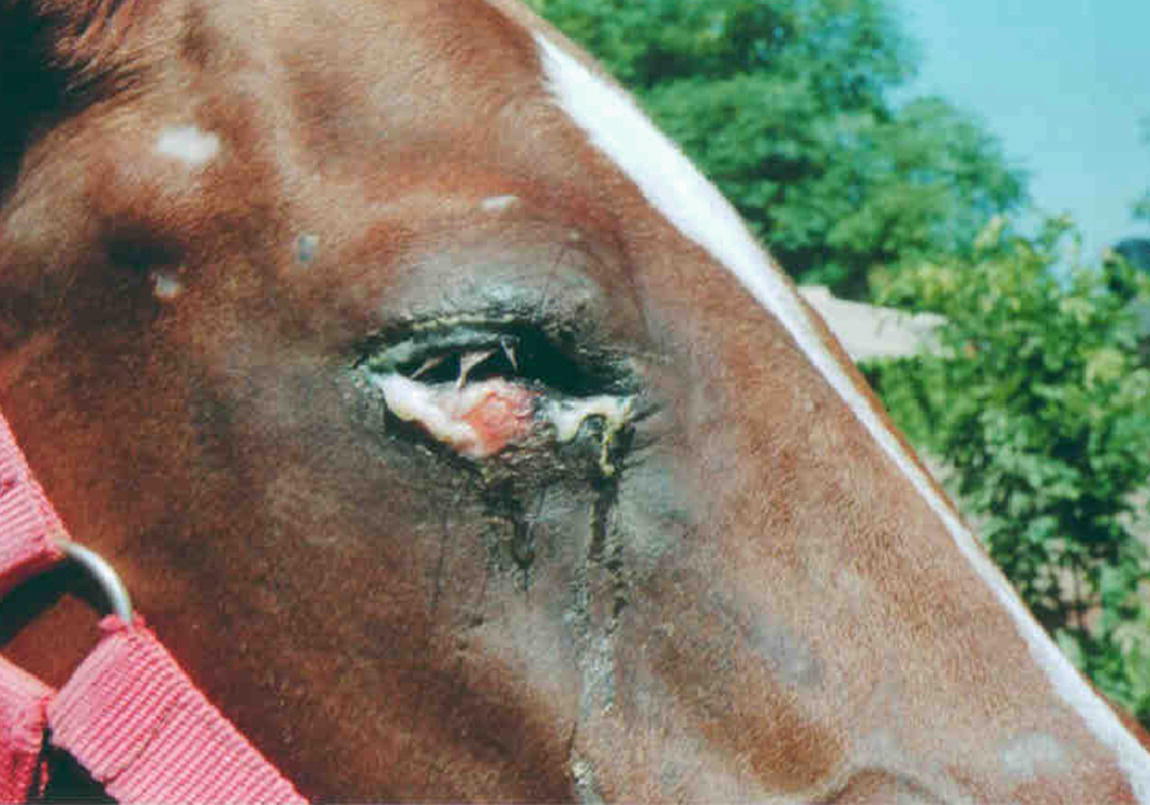
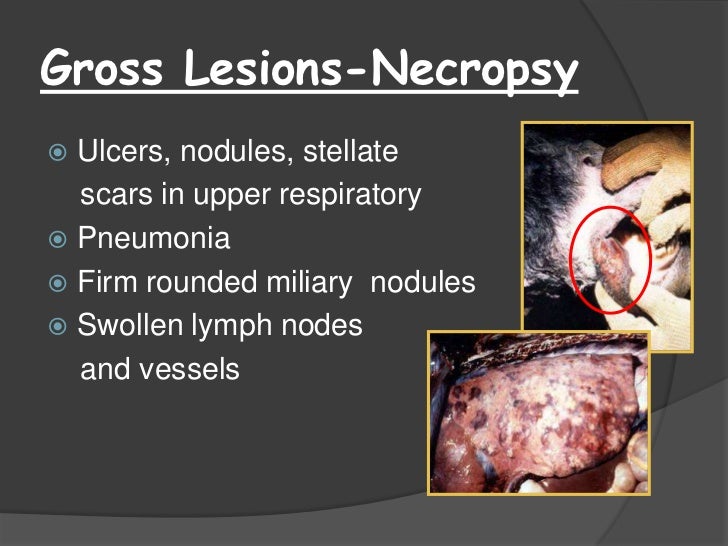
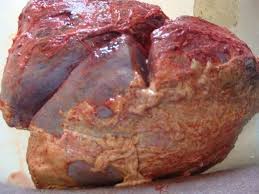
Glanders is a highly infectious zoonotic disease of equids horses donkeys mules caused by the bacterium Burkholderia mallei Cárdenas et al 20. Additional symptoms may include excessive tearing of the eyes light sensitivity ulcers and diarrhea loose stoolpoop. Symptoms of glanders commonly include.
The disease mainly affects horses donkeys and mules. The symptoms depend on the route of infection.
Fever with chills and sweating Muscle aches Chest pain Muscle tightness Headache Nasal discharge Light sensitivity sometimes with excessive tearing of the eyes.
The disease is transmissible from animal to man and from man to man. Coughing discharge from the nose fever. Glanders is primarily a disease affecting horses but it also affects donkeys mules and can be contracted by goats dogs and cats. Glanders is a highly infectious zoonotic disease of equids horses donkeys mules caused by the bacterium Burkholderia mallei Cárdenas et al 20. If left untreated in humans the disease is fatal in 2-4 weeks and the causative organism as a result is considered a potential bioterrorism agent. It is primarily a. It may also be inhaled via infected aerosols or dust contaminated by infected animals. Mallei from solipeds to humans appears to be. Glanders may manifest in humans as localized pulmonary bloodstream or chronic infections CDC.
The bacteria enter the body through cuts or abrasions in the skin and through mucosal surfaces such as the eyes and nose. Mallei from solipeds to humans appears to be. Secondarily humans may become infected through contact with diseased animals or by inoculation while handling diseased tissues and making laboratory cultures of the causal bacillus. Glanders is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Burkholderia mallei. Glanders may manifest in humans as localized pulmonary bloodstream or chronic infections CDC. It also affects donkeys and mules and can be naturally contracted by other mammals such as goats dogs and cats. Transmission is uncommon even in the setting of frequent close contact with infected animals however occupational exposure is a key risk factor.






































Post a Comment for "Glanders Disease In Humans"